Beef Round Round Tip 2 Cov Knuckle
Beef The Major Cuts
Round
Round Steak
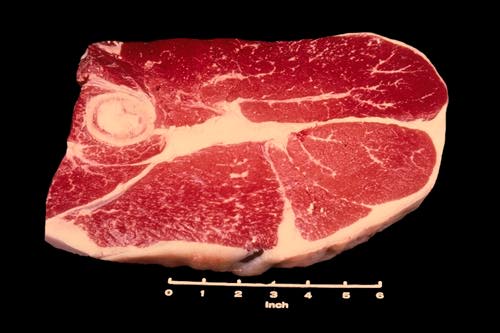
TThis steak is identified by the round leg bone and three muscles. At the top of the screen is the top round, at the lower left is the bottom round, and lower right is the eye of the round.
Cooking Recommendations
Braise or Panfry
Boneless Rump Roast
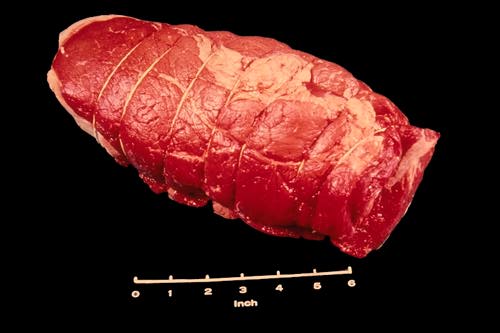
When the rump is removed, boned, rolled and tied, a retail cut called the Beef Round Rump Roast is made. This represents a cut only moderately tender, moist heat is often used. However with a cut from choice and prime cattle, it is often cooked with dry heat.
Cooking Recommendations
Roast or Braise
Top Round Steak
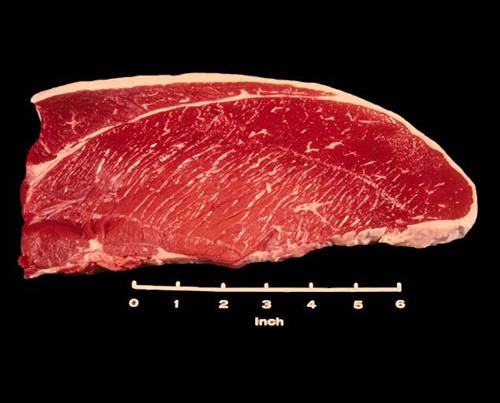
The Top Round Steak is the most tender of the various round steaks. This boneless steak consists of a large muscle called the top or inside round. Note the cover fat on the curved top surface, the cut surface on the left side, and connective tissue along the bottom.
Cooking Recommendations
Broil, Panbroil, or Panfry
Bottom Round Steak

The Beef Bottom Round Steak contains muscles which are less tender than the top round muscle. The two muscles of this steak are the eye of the round on the left and the bottom round on the right. Note the heavy band of connective tissue separating the muscles. Moist heat is recommended for this steak.
Cooking Recommendations
Braise
Eye Round Steak
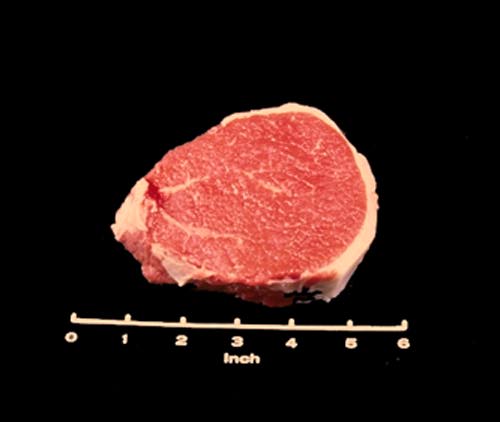

The Beef Round Eye Round Steak is a small round boneless steak. It usually has a layer of external fat on two sides.
Cooking Recommendations
Braise, Grill, Panbroil, or Panfry
Tip Roast
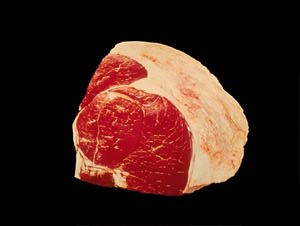
The Beef Round Tip Roast is a rolled and tied roast that is identified by four individual muscles within one large muscle mass.
Cooking Recommendations
Roast
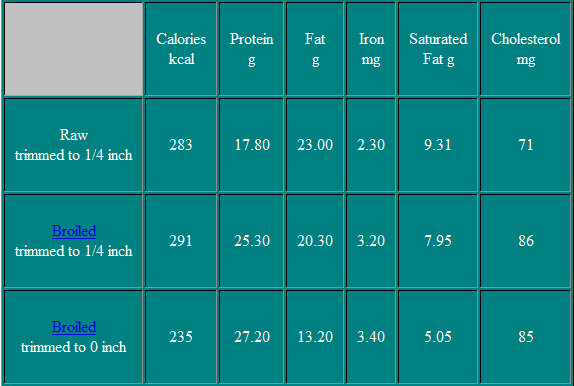
Nutritional Information
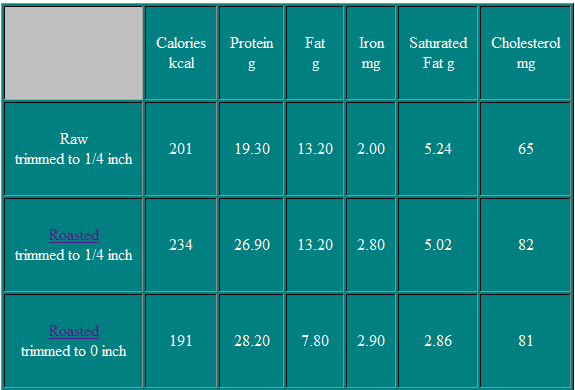
Tip Steak
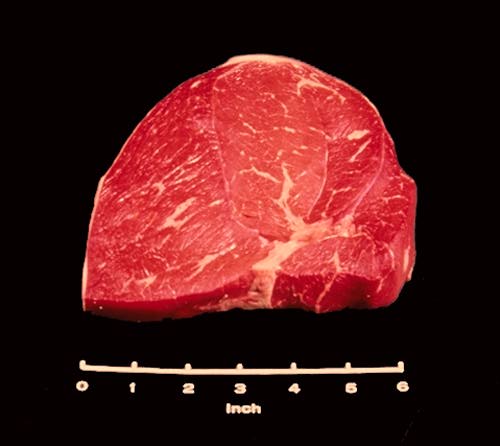
The Tip Steak is cut from the tip roast. Like the roast this steak is identified by four individual muscles within on large muscle mass.
Cooking Recommendations
Broil, Panbroil, or Panfry
Heel of Round
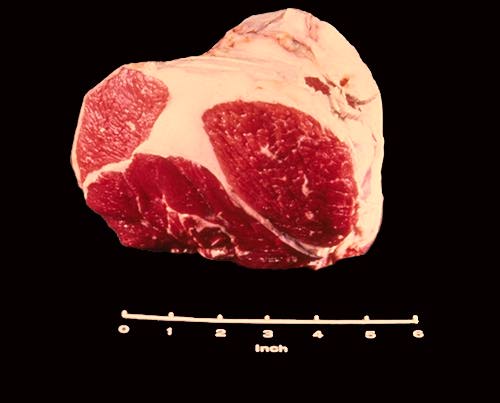

The Beef Heel of Round represents a cut from the beef round immediately above the hock. This roast is composed of many small muscle groups, has a lot of seam fat, and is one of the least tender cuts of beef.
Cooking Recommendations
Braise
Loin
Top Loin Steak
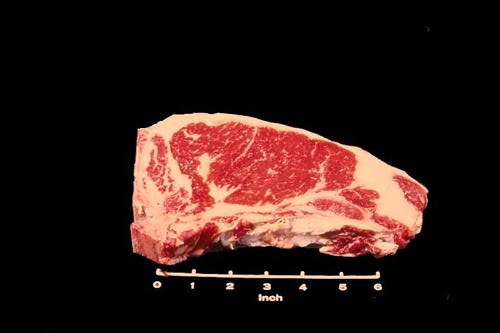
The Beef Loin Top Loin Steak is the first type of steak cut from the beef loin. It is cut from the end of the beef loin which contains the last or 13th rib. This steak is identified by the large eye muscle, the rib bone, and part of the backbone.
Cooking Recommendations
Broil, Grill, Panbroil,or Panfry
Nutritional Information
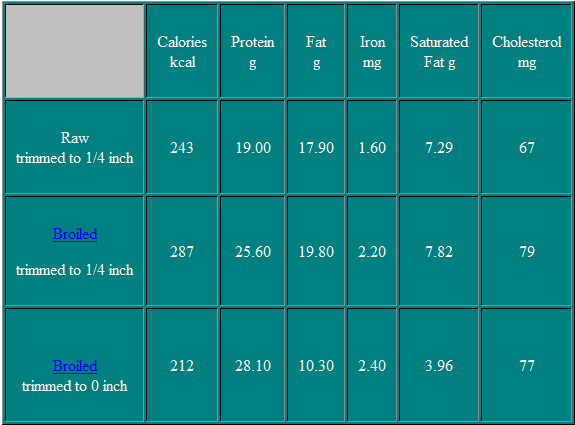
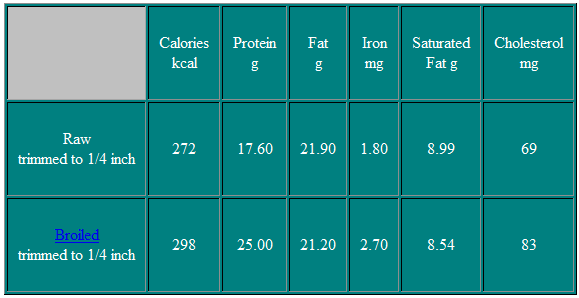
T-Bone Steak
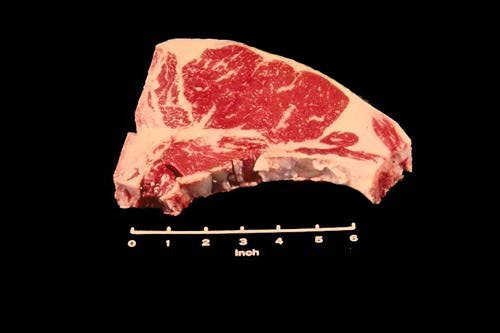
This steak has the characteristic "T" shaped vertebrae and the large eye muscle. The smaller muscle located below the T-bone is the tenderloin.
Cooking Recommendations
Broil, Grill, Panbroil,or Panfry
Nutritional Information
Top Loin Steak, Boneless

The boneless large eye muscle from the T-bone steak is called the Beef Loin Top Loin Steak, Boneless.
Cooking Recommendations
Broil, Grill, Panbroil,or Panfry
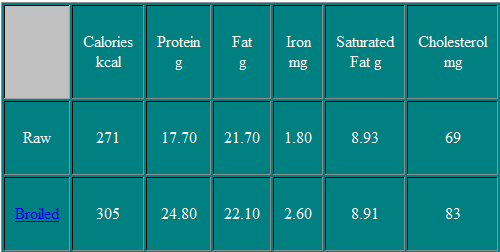
Porterhouse Steak
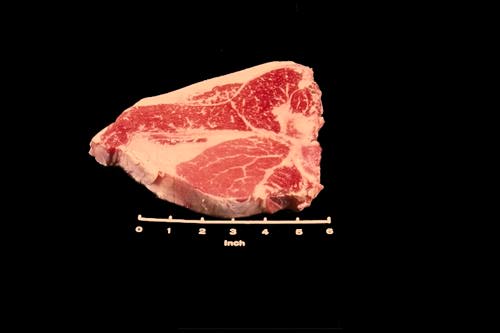
The Porterhouse Steak is similar to the beef loin T-bone steak. However the tenderloin muscle is much larger and an extra muscle is located in the center of the porterhouse steak on the upper side.
Cooking Recommendations
Broil, Grill, Panbroil,or Panfry
Nutritional Information
Tender Loin Steak
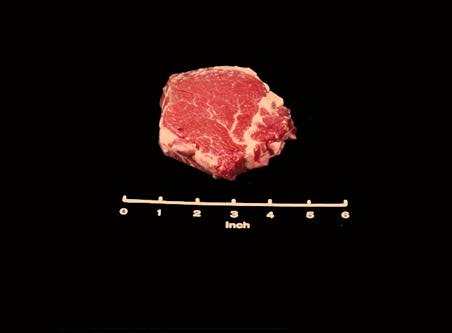
The most tender retail cut from the entire beef carcass is the Beef Loin Tenderloin Steak. This steak has a fine texture, is circular in shape and is usually about three inches in diameter.
Cooking Recommendations
Broil, Grill, Panbroil, or Panfry
Nutritional Information
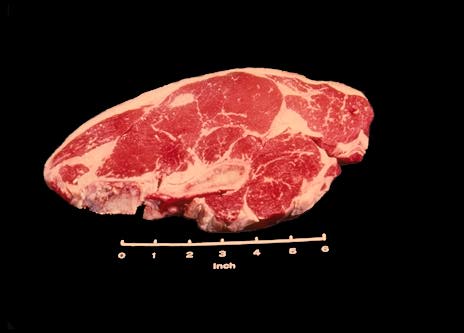
Sirloin Steak Pin Bone

The Beef Loin Sirloin Steak, Pin Bone is the first cut from the sirloin area of the beef loin. This steak looks much like the beef loin T-bone and porterhouse steaks in that it contains the T-bone the large eye muscle and the tenderloin muscle. However, it also contains an oval-shaped bone which you can see in the upper left corner of the steak. This bone is called the pin bone and is the tip portion of the hip bone.
Cooking Recommendations
Broil, Grill, Panbroil, or Panfry
Nutritional Information

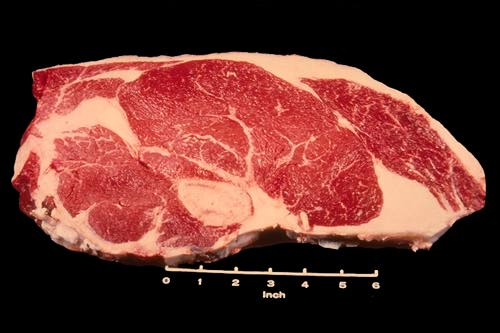
Sirloin Steak Flat Bones
The Beef Loin Sirloin Steak, Flat Bone is the least valuable type of sirloin steak if both the flat hip and backbones are left in the steak.
Cooking Recommendations
Broil, Grill, Panbroil, or Panfry
Sirloin Steak Round Bones
The Sirloin Steak, Round Bone is located further back on the sirloin area of the beef loin. This particular sirloin steak has the greatest amount of lean and the least amount of bone.
Cooking Recommendations
Broil, Grill, Panbroil, or Panfry
Sirloin Steak, Wedge Bone
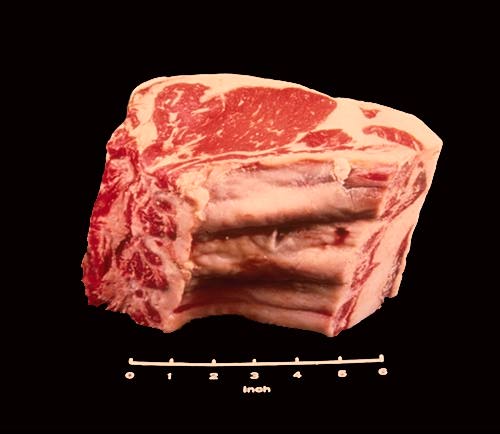

The sirloin steak nearest the wholesale beef round is called the Beef Loin Sirloin Steak, Wedge Bone. Only one bone is usually seen, a wedge-shaped bone at the bottom of the cut near the center.
Cooking Recommendations
Broil, Grill, Panbroil, or Panfry
Sirloin Steak, Boneless
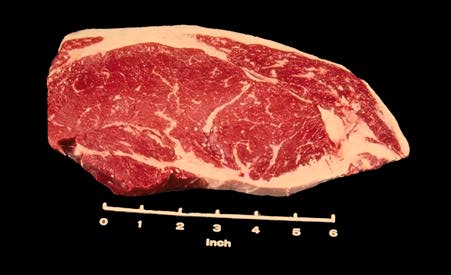
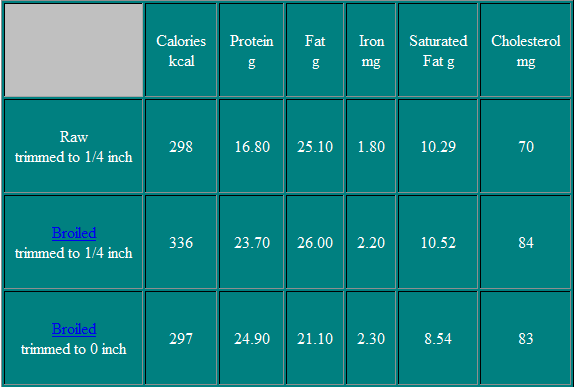
The Beef Loin Sirloin Steak, Boneless is an excellent steak for broiling and is made by removing all of the bones from any of the other types of sirloin steaks.
Cooking Recommendations
Broil, Grill, Panbroil,or Panfry
Rib
Rib Roast Small End

The Beef Rib Roast, Small End, contains several ribs, a protion of the backbone and one large muscle, the rib eye
Cooking Recommendations
Roast, or Grill by indirect heat
Nutritional Information
Beef Rib Roast Roll
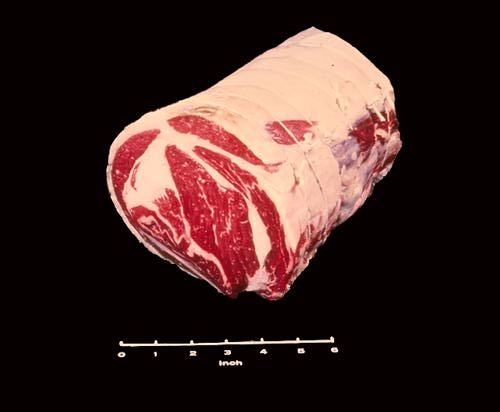

The bones of the beef rib roast are sometimes removed and the cut is tied in a roll with string as shown in this slide. When this is done the cut is known as a Beef Rib Roast,Boneless. Note that the rib eye muscle runs through the center of the roast and is surrounded by smaller muscles.
Cooking Recommendations
Roast, or Braise
Rib Steak Large & Small End
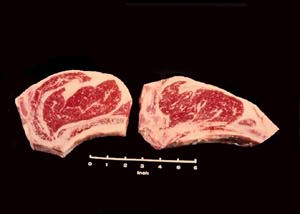
On the right is a Beef Rib Steak, Small End. The cut on the left is a Beef Rib Steak, Large End. Both steaks contain a rib and portion of the backbone. Steaks from the small end of the beef rib contains only the large rib eye muscle while steaks from the large end also contains one or more smaller muscles.
Cooking Recommendations
Broil, Grill, Panbroil,or Panfry
Rib Eye Steak

The Beef Rib Eye Steak come from the large end of the beef rib and is made by removing back and rib bones.
Cooking Recommendations
Broil, Grill, Panbroil,or Panfry
Chuck
Chuck Blade Roast
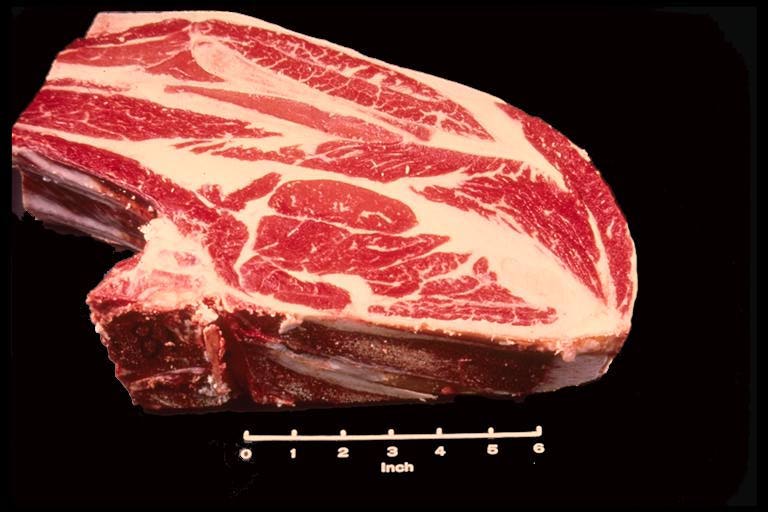

This large roast contains many small muscles and is easily identified by the blade bone located in the upper center of this cut. Note also that rib bones and a portion of the backbone are located along the lower left portion of the cut. However, these bones may be removed from this large roast before it is packaged and put in the meat counter at the local supermarket.
Cooking Recommendations
Braise, or Roast
Nutritional Information
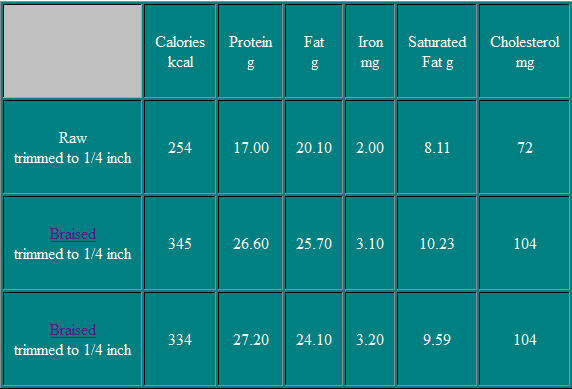
Chuck Blade Steak
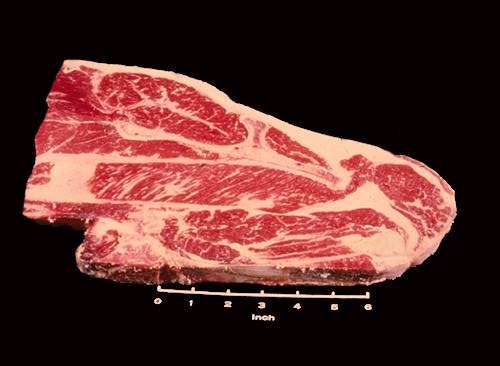
The Beef Chuck Blade Steak is similar to the beef chuck blade roast. It is usually cut less than one inch thick. The blade bone shown in this slide has the typical shape of the "sevenbone", a term frequently used in the meat trade.
Cooking Recommendations
Braise, Grill, or Broil
Chuck Arm Roast

The Beef Chuck Arm Roast is identified by its thickness as a roast, the large round bone in the center of the cut and the many small muscles of which it is made. This roast may or may not have a cross cut rib bones showing but if present would be at the bottom of the picture.
Cooking Recommendations
Braise, Grill, Panbroil, Panfry, or Broil
Nutritional Information

Chuck Arm Steak

The Chuck Arm Steak is similar to the Chuck Arm Roast, thickness is the only difference. Note the round bone surrounded by many small muscles. This steak will usually not have any rib bones showing.
Cooking Recommendations
Braise
Cross Rib Pot Roast
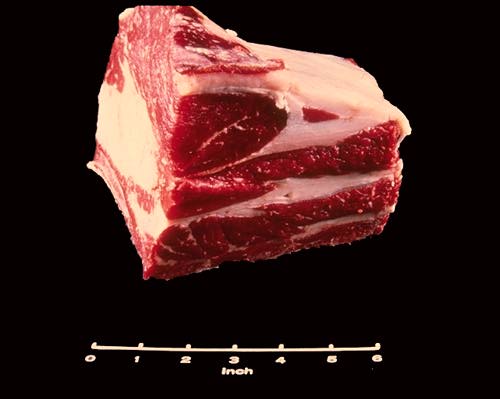
This square cut roast comes from the lower corner of the beef chuck. In addition to its square shape this cut is identified by portions of two or three ribs on the underneath side. Note also, the large amount of seam fat located between the muscles.
Cooking Recommendations
Braise, or Roast
Flank & Plate
Flank Steak
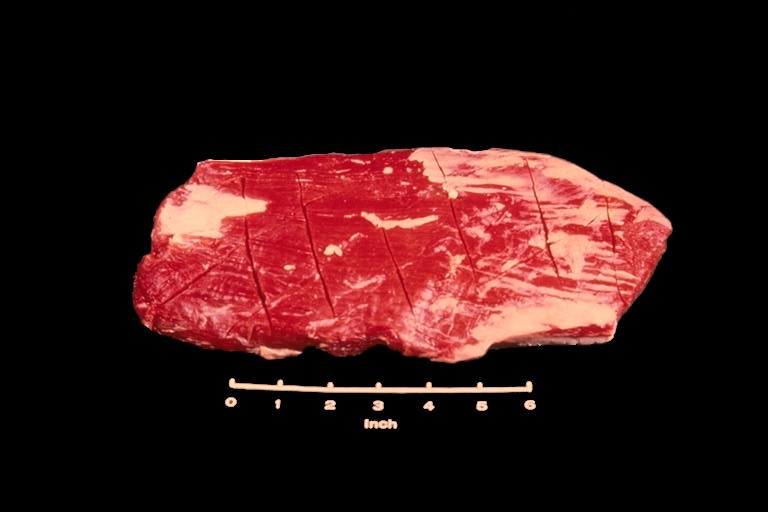
The Beef Flank Steak is the only steak in the carcass containing an entire large muscle. Also, although most other steaks are cut across the muscle fibers, the flank steak fibers run the full length of the steak. To help tenderize these long fibers, you will notice the knife scores across the cut. Since the flank steak is one of the less tender steaks, it should be cooked with moist heat cookery.
Cooking Recommendations
Braise, Grill, Stirfry, or Broil
Brisket & Foreshank
Beef Shank Cross Cut
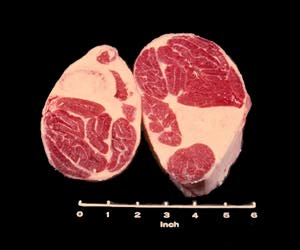
The Beef Shank Cross Cut is identified by a cross section of the arm bone and many very small muscles, each surrounded by connective tissue.
Cooking Recommendations
Braise, or Cook in Liquid
Beef Brisket, Whole, Boneless

The Beef Brisket is a very course textured muscle. The heavy layer of fat and the sternum or breast bone have been removed. Due to the course texture of this muscle, cooking in liquid is recommended.
Cooking Recommendations
Braise, or Cook in Liquid
Nutritional Information
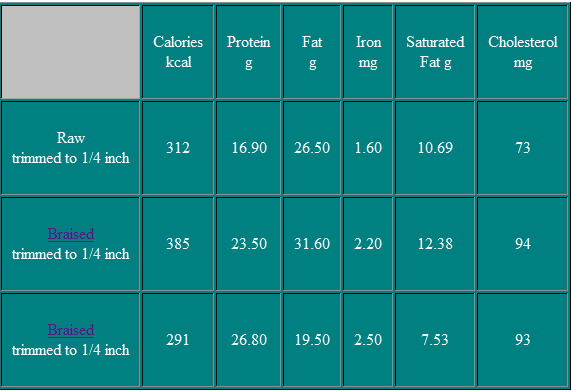
Short Ribs

Short Ribs are small cubes containing a section of the rib bone and thin layers of muscles. The muscles of the chest perform considerable work and are therefore not very tender.
Cooking Recommendations
Braise, or Cook in Liquid
Nutritional Information
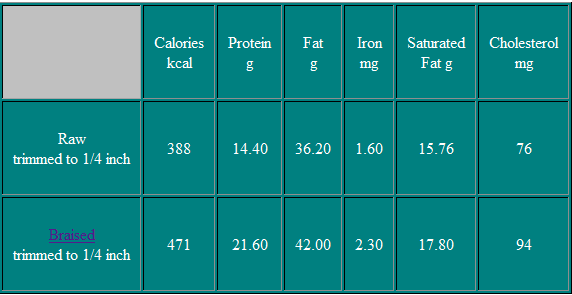
Various Cuts
Ground Beef
Cubed Steak
Beef for Stew
This large roast contains many small muscles and is easily identified by the blade bone located in the upper center of this cut. Note also that rib bones and a portion of the backbone are located along the lower left portion of the cut. However, these bones may be removed from this large roast before it is packaged and put in the meat counter at the local supermarket.
Cooking Recommendations
Nutritional Information

Cubes for Kabobs
This large roast contains many small muscles and is easily identified by the blade bone located in the upper center of this cut. Note also that rib bones and a portion of the backbone are located along the lower left portion of the cut. However, these bones may be removed from this large roast before it is packaged and put in the meat counter at the local supermarket.
Cooking Recommendations
Nutritional Information
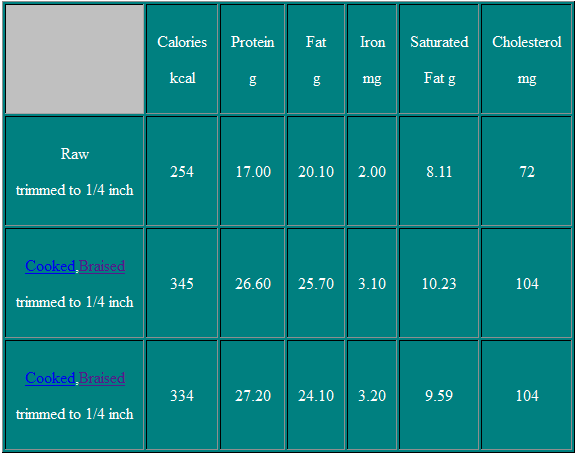
Variety Cuts
Source: https://animalscience.unl.edu/beef-meat-identification
0 Response to "Beef Round Round Tip 2 Cov Knuckle"
Post a Comment